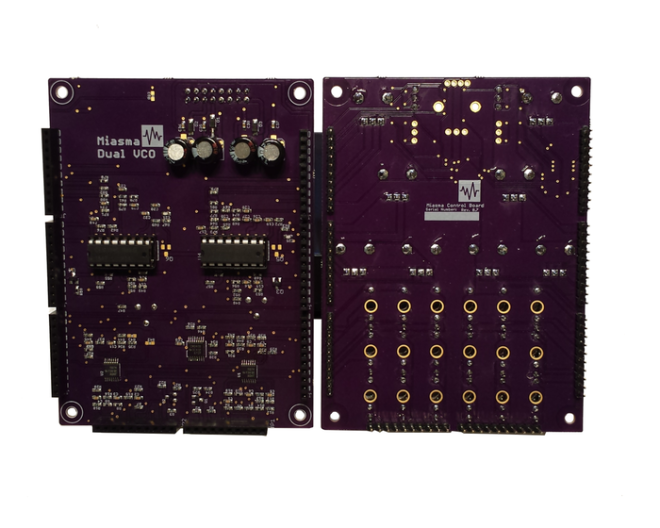
Miasma is a pure analog oscillator module based on the Curtis CEM3340 chips used in legendary ’80s synths, with new & innovative signal patching:
Miasma: Classic Dual Voice Eurorack Synthesizer Module
We designed the Miasma Voltage Controlled Oscillator (VCO) to bring that classic ’80s synthesizer sound back to Eurorack modular systems. We just couldn’t find any currently available oscillators with the sound textures and capabilities that we wanted, so we had to design our own; and now you get to own one as well.
There are many unique capabilities built into Miasma that you won’t find in any other oscillator module, like the built-in patching and cross modulation structures that make Miasma so flexible in your rack. However, it’s all about the sound – so let’s start with some Miasma audio samples, before we go into the technical details of how we make that sound possible (best listening with Headphones!)